CBT is the most recommended form of evidence based therapy today for improving one's mood and relationships!
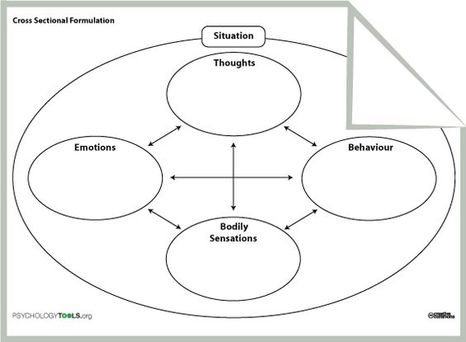
Mental health problems such as mood disorders, eating disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder, hoarding disorder, borderline personality, trauma, substance abuse, and marital distress have been treated effectively in research using CBT. A popular approach called exposure therapy is often used to desensitize individuals from perceived fear, threat, or anxiety. Discussing or visualizing the feared topic, thought, or situation over time and at length results in reductions of the anxiety and avoidance behaviors. Some exposure techniques like Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) induce the client into a dream simulation state, using side-to-side eye movements, to enhance emotional processing during virtual exposure to past traumatic events.
Discussing the feared topic, thought, or situation repeatedly over time results in reductions of anxiety
Mindfulness is a technique used to increase awareness of one’s inner reality and emotional state. Practicing mindfulness increases the focus on the mind body connection. Thoughts can be triggers for distressing physiological and emotional reactions in the body. Mindfulness techniques can be used as exposure to ones own disturbed internal environment. Mindfulness exercises, such as deep breathing, can be very relaxing and useful as a tool to shift the autonomic nervous system from sympathetic (fight and flight) activation to parasympathetic (resting) state. An individual at the mercy of anxiety will find tremendous relief discovering how to use a mindfulness “dimmer switch”. Emotion regulation is a problem solving approach that teaches various strategies to reduce emotional intensity. A person may be asked to write a pro’s and con’s list for continuing behaviours that trigger negative emotions. Alternatively, they may be asked to act in an opposite way than they often choose to break the unproductive pattern. For example, a depressed person may be asked to go out and socialize even though he feels like isolating himself.
Emotion regulation strategies are used to reduce overwhelming emotional experiences
Distress tolerance is a problem solving approach often employed for suicidal or self-harming individuals. Solutions that prevent bodily harm are practiced to assist the person to tolerate enduring and intensely painful emotional experiences. One example, is to have the individual squeeze ice cubes or submerse her face in a bowl of ice cold water. Another could be the use of tapping techniques on pressure points to elicit a temporary emotional release. The goal is to bring focus away from the emotionally painful thoughts by using harmless physical sensations as a distraction. Emotions arrive in waves and these techniques allow people to shorten the wavelength.
Physical sensations are used to distract and shorten the waves of emotional pain.
Response shaping is an operant behavioral technique that uses a reward system to gradually teach a new behavior while replacing an undesirable behavior. For example, a chart showing a desired behavioral step can be regularly checked and reinforced with gold stickers until the next step in taught. Respondent behavior therapy focuses on reflex like connections demonstrated in the experiments conducted by Pavlov on his dogs. Pavlov showed his dogs steak to make them salivate and then rang a bell. After a few repetitions for a number of days, the bell ringing stimulus alone would produce the salivation response. Negative emotions and their antecedent behaviors function in the same way. The sound of a backfiring car can elicit tremendous fear and alarm in a war veteran who was wounded in combat by gun fire. Emotions and antecedent stimuli are identified and uncoupled using demonstrations of safety in the presence of both the conditioned stimulus and conditioned response.
The sound of a backfiring car alone can elicit tremendous fear and alarm in a war veteran who was wounded in combat.
Cognitive restructuring is a central strategy in CBT, where people are made to examine their thoughts, check for errors/ accuracy of the thought, and the effect the thought has on mood or interpersonal relationships. CBT also aims to delve deeper into the psyche of clients to uncover core thoughts, values, and/or beliefs. These core beliefs are very important as they are strongly held and, if factually erroneous, can distort a client’s perception. For example, a person may believe that she is unlovable. While holding this core belief, she may choose to recall experiences of rejection, abandonment, and disappointment in relationships instead of seeing a balanced view of reality. Accepting that others do act loving at times would be difficult for this person as it would counter her set core belief about self and others.
Core beliefs are very important as they are strongly held and, if factually erroneous, can distort a person's perception
Cognitive behavioral therapy is a broad analytical therapeutic approach equipped with many behavioral tools. The research on its effectiveness also varies, but is quite favorable for many mental health disorders. It can be used alone or in combination with other therapies. CBT is client-centered approach that uses useful mood tracking tools and outcome measures. It keeps therapy interesting, relevant, and focused by helping people keep track of their progress in improving mood and functioning.









 RSS Feed
RSS Feed